The 2016 Bitfinex Hack: A Comprehensive Analysis
The 2016 Bitfinex hack represents one of the most significant security breaches in cryptocurrency history, resulting in the theft of approximately 120,000 bitcoins valued at roughly $72 million at the time. This incident has become a landmark case study in cryptocurrency security, digital forensics, and the legal pursuit of cybercriminals. The hack’s aftermath spanned years, culminating in arrests, guilty pleas, and the largest cryptocurrency seizure in history. What follows is a detailed analysis of this watershed event in cryptocurrency security history, examining its timeline, technical aspects, attribution, and long-term implications.

The Hack Timeline and Initial Response
The Bitfinex cryptocurrency exchange was breached on August 2, 2016, in what was then the second-largest bitcoin hack ever recorded. In less than two hours, approximately 119,756 bitcoins were stolen from the exchange and distributed across 2,075 addresses under the control of the hackers. The rapid theft immediately sent shockwaves through the cryptocurrency market, causing bitcoin’s trading price to plunge by approximately 20%, which ironically reduced the value of the stolen funds from $72 million to around $58 million.
Upon discovering the breach, Bitfinex took immediate action by halting all bitcoin withdrawals and trading activities on the platform. The exchange announced that it was tracking the perpetrators of the hack while simultaneously developing a strategy to address the losses. In an unprecedented move, Bitfinex decided to socialize the losses across all account holders, implementing a 36.067% reduction to all customer accounts, regardless of whether they were directly affected by the hack. In exchange for this reduction, customers received BFX tokens at a value of $1 each, which Bitfinex promised to gradually redeem as the company recovered financially.
The weeks following the hack saw Bitfinex scrambling to restore operations and customer trust. On August 17, 2016, the exchange announced it had retained Ledger Labs to investigate the security breach and improve their system design going forward. By September 1, 2016, Bitfinex began its redemption process by announcing it had bought back over 1.1812% of the BFX tokens. This redemption process continued incrementally over the following months, with Bitfinex announcing various redemption percentages at regular intervals. By April 3, 2017, approximately eight months after the hack, Bitfinex had fully redeemed 100% of the outstanding BFX tokens, effectively making customers whole on their losses.
Technical Details of the Breach
The technical aspects of the Bitfinex hack reveal significant vulnerabilities in what was supposed to be a robust security architecture. Bitfinex employed BitGo’s multi-signature security solution, which required multiple approvals for transactions, theoretically providing enhanced protection against unauthorized withdrawals. Despite this security measure, the hackers managed to compromise the system and authorize approximately 2,000 fraudulent transactions directing funds to wallets under their control.
The post-hack security report created by Ledger Labs and later obtained by the Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) detailed numerous security lapses at Bitfinex. These included failures to follow industry best practices, inadequate logging procedures, and failure to implement proper whitelist controls. The report specifically mentioned poor management of “Giancarlo” keys, suggesting this may have been a critical vulnerability exploited during the attack[6]. IP address analysis from the report also suggested that the hack originated from Poland, providing investigators with an initial geographic lead.
A particularly concerning aspect of the breach was the apparent circumvention of transaction limits. Critics questioned why BitGo allowed around 120,000 BTC to be withdrawn from thousands of Bitfinex users in just three hours without triggering security protocols. In response to these concerns, BitGo’s co-founder and CEO Mike Belshe stated that their systems were not breached and their software functioned correctly during the attack. Belshe emphasized that “the Bitfinex configuration was unique and other BitGo customers do not need immediate changes,” suggesting that the vulnerability was specific to how Bitfinex had implemented their security system rather than a flaw in BitGo’s technology itself.
Attribution and Legal Proceedings
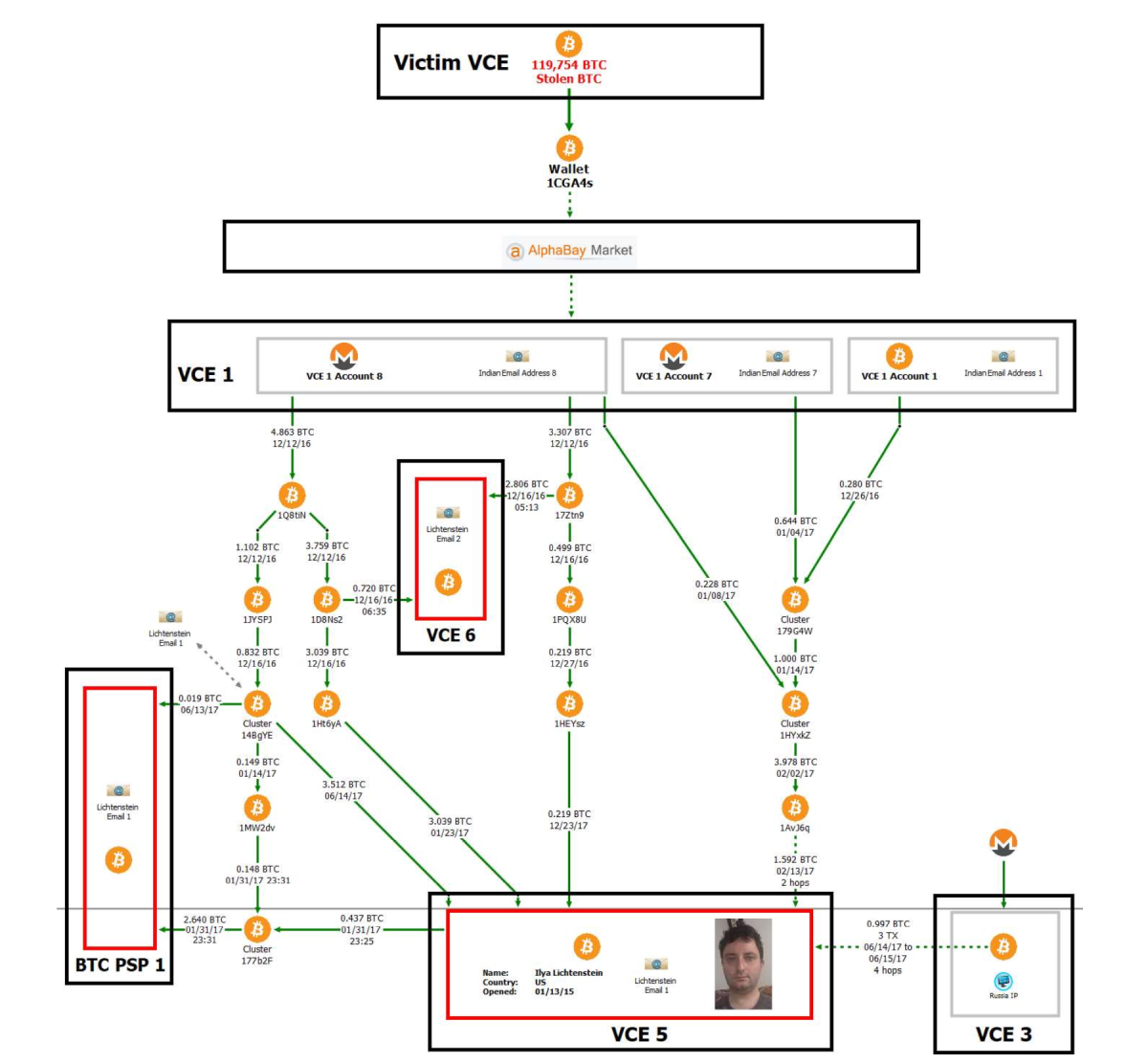
For nearly six years, the identity of the Bitfinex hackers remained unknown. However, in February 2022, the investigation reached a dramatic turning point when the United States government announced it had seized approximately 94,643 bitcoins (worth $3.6 billion at the time) connected to the 2016 hack. This marked the largest financial seizure in the Department of Justice’s history.
The breakthrough came when investigators managed to decrypt a file owned by Ilya Lichtenstein that contained addresses and private keys associated with the stolen funds. Following this discovery, authorities arrested Lichtenstein, then 35, and his wife Heather Morgan, 31, charging them with conspiracy to launder the stolen bitcoin[7]. The investigation revealed that the couple had attempted to launder the proceeds through a complex web of cryptocurrency transactions and fraudulent identities. Over 2,000 fraudulent transactions were used to move the stolen bitcoin, and Lichtenstein had deleted access credentials and log files on Bitfinex’s servers to cover his tracks[4]. The laundering operation involved Eastern European bank accounts and cryptocurrency mixing services designed to obscure the source of the funds.

In August 2023, after a lengthy legal process, Lichtenstein admitted to committing the theft, and both he and Morgan pleaded guilty to money laundering charges. The legal proceedings culminated in November 2024 when Lichtenstein was sentenced to five years in a US prison for his involvement in the hack and subsequent money laundering. Morgan received an 18-month prison sentence for fraud and conspiracy charges. In a separate development, in July 2023, Bitfinex worked with the Department of Homeland Security to recover an additional $315,000 in cash and cryptocurrencies connected to the 2016 breach, which the exchange promised to redistribute to holders of their Recovery Right Tokens.
Security Failures and System Vulnerabilities
The Bitfinex hack illuminated several critical security vulnerabilities that allowed the attackers to successfully compromise the exchange. According to the internal Ledger Labs report, Bitfinex failed to implement several fundamental security practices that could have prevented or limited the scope of the attack. The absence of adequate logging procedures meant that suspicious activities might not have been properly monitored or flagged for review. Similarly, the failure to implement a robust whitelist system allowed the attackers to withdraw funds to unauthorized addresses without additional verification steps.
The management of private keys appears to have been a particularly significant vulnerability. The report specifically highlighted poor management of “Giancarlo” keys, suggesting this may have been a central vector for the attack. In a multi-signature security system like the one Bitfinex employed, proper key management is essential, as compromising a sufficient number of keys would allow attackers to authorize transactions without legitimate approval.
One of the most perplexing aspects of the breach was the apparent failure of transaction monitoring and limits. The fact that approximately 120,000 bitcoins could be withdrawn in such a short period without triggering security alerts points to significant gaps in the exchange’s risk management systems. While BitGo maintained that their systems functioned correctly, the incident highlighted the importance of implementing appropriate transaction limits and monitoring unusual activity patterns, especially for high-value withdrawals.
Post-Breach Mitigation and Recovery Efforts
In the aftermath of the hack, Bitfinex implemented several measures to mitigate the damage and rebuild customer trust. The most controversial decision was the socialization of losses across all user accounts through a 36.067% “haircut” regardless of whether their specific accounts had been compromised. This approach was justified under the premise that targeted reductions only to affected accounts would have resulted in insolvency for many users and potentially the exchange itself.
To compensate customers for these reductions, Bitfinex issued BFX tokens, which served as debt tokens that the company promised to redeem over time. The exchange committed to using future profits to gradually buy back these tokens until all customers were made whole. True to this commitment, Bitfinex implemented a series of redemptions beginning on September 1, 2016, with a 1.1812% redemption of outstanding BFX tokens. These redemptions continued at regular intervals, with increasing percentages as the company recovered financially. By April 3, 2017, Bitfinex had redeemed 100% of the outstanding BFX tokens, effectively erasing the debt to its customers less than a year after the hack.
However, controversy emerged regarding how evenly the haircut was applied. Former Bitfinex Director Zane Tackett claimed that while Coinbase did receive a haircut, it was smaller than that applied to other clients, contradicting Bitfinex’s initial statement that “losses must be generalized across all accounts and assets”. This discrepancy raised questions about the fairness of the loss socialization approach and the company’s transparency in implementing it.
Blockchain’s Role in Criminal Investigation
The Bitfinex case has become a landmark example of how blockchain technology’s inherent transparency can serve as a powerful forensic tool for law enforcement. Despite the sophisticated methods employed by the hackers to launder the stolen bitcoin, the immutable nature of blockchain transactions provided investigators with a permanent record of fund movements. Every transaction from the initial theft to subsequent attempts at laundering was recorded on the public ledger, creating an audit trail that investigators could follow.
When announcing the 2022 seizure of $3.6 billion in stolen bitcoin, law enforcement agencies highlighted how the blockchain’s permanence contributed significantly to the recovery of assets. The transparency of the blockchain allowed investigators to clearly establish that the funds taken from Bitfinex were now in the possession of the US government. This case demonstrated that while cryptocurrency might provide initial anonymity, the permanent nature of blockchain records makes it an increasingly challenging medium for long-term money laundering.
The recovery effort involved a joint operation between multiple law enforcement agencies, including the IRS Criminal Investigation unit, the FBI, and Homeland Security Investigations. Their success in recovering approximately 94,643 bitcoins (nearly 80% of the stolen funds) marked the largest recovery of assets from a theft in history. This achievement has significant implications for cryptocurrency security, sending a clear message that law enforcement has developed the technological capabilities and investigative techniques necessary to track and recover stolen digital assets, even years after the initial theft.
Lessons Learned and Industry Impact
The Bitfinex hack prompted significant changes in cryptocurrency exchange security practices and regulatory approaches. The incident highlighted several critical lessons that have shaped industry standards in the years since. First and foremost, it demonstrated that even sophisticated multi-signature security systems can be compromised if not implemented and monitored correctly. The hack underscored the importance of proper key management, comprehensive logging, transaction monitoring, and whitelist controls as essential components of a robust security architecture.
For cryptocurrency users, the Bitfinex case emphasized the importance of personal security measures. Security experts now strongly recommend practices such as conducting thorough due diligence before engaging with any platform, utilizing cold storage options like hardware wallets for long-term holdings, maintaining secure backups of private keys or seed phrases, enabling Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) wherever possible, and using strong passwords along with VPNs for added security.
The incident also accelerated regulatory developments around cryptocurrency exchanges. In response to this and other high-profile hacks, various jurisdictions began developing more comprehensive regulatory frameworks for cryptocurrency exchanges. For example, Japan, which had already begun developing regulations following the earlier Mt. Gox scandal, implemented a framework requiring exchanges to follow security standards similar to traditional financial institutions. These regulatory changes have gradually pushed the industry toward higher security standards and greater accountability.
Conclusion
The 2016 Bitfinex hack stands as one of the most significant security incidents in cryptocurrency history, not only for its scale but also for its far-reaching implications. From the initial theft of 119,756 bitcoins to the dramatic arrest and conviction of the perpetrators nearly eight years later, this case has provided valuable insights into cryptocurrency security, forensic investigation, and the evolving capabilities of law enforcement in the digital asset space.
The security failures that enabled the hack—inadequate logging, poor key management, and ineffective transaction monitoring—offer crucial lessons for cryptocurrency exchanges and users alike. Meanwhile, the subsequent investigation demonstrates that despite the perceived anonymity of cryptocurrency, blockchain’s inherent transparency ultimately creates significant challenges for would-be thieves attempting to launder stolen funds over the long term.
As the cryptocurrency industry continues to mature, the Bitfinex hack serves as both a cautionary tale about the importance of robust security measures and a testament to the increasing sophistication of digital forensics and law enforcement capabilities. The case has fundamentally altered how exchanges approach security and how users perceive risks in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, contributing to the development of stronger safeguards and more effective recovery mechanisms for the industry as a whole.